State in Decline, Employment in RI Cities and Towns: Johnston
At 12.9% (not seasonally adjusted) in March, Johnston’s unemployment rate was well above the overall state percentage of 11.8%, but it shares the trend story of many Rhode Island cities and towns.
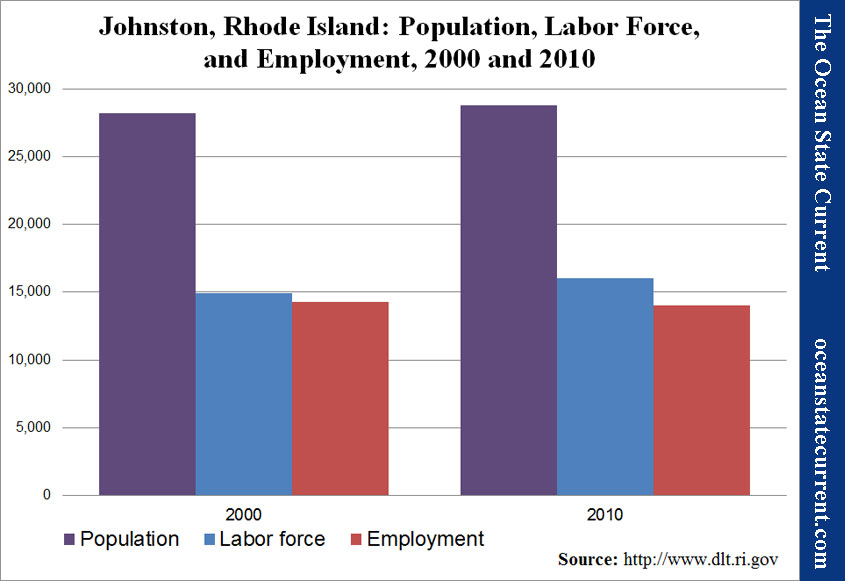
From the year of the 2000 U.S. Census to 2010, Johnston’s population grew a bit (2.0%), but its total labor force (those working or looking for work) grew quite a bit (7.0%). Meanwhile, the number of its residents counting as unemployed fell 1.8%. That drop was actually less than the average RI city or town, but the leap in the number of people looking for work exacerbated the unemployment.
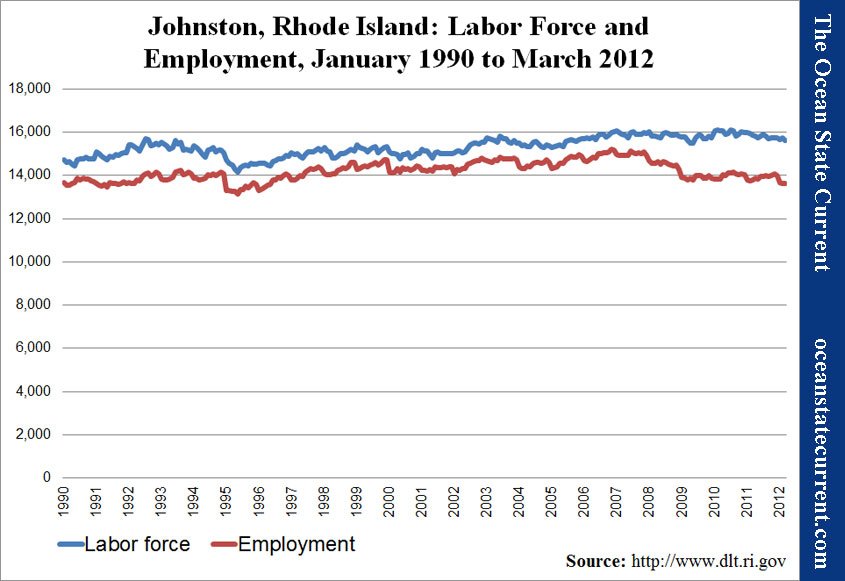
Looking more closely at labor force and employment, over the twenty-two years of data that the RI Dept. of Labor and Training makes available online, presents another familiar story (albeit more egregious than over the rest of the state). The town’s labor force is higher than its average, while its employment is lower, leaving the number of employed residents near its all-time high.
In the following chart, unemployment is represented as the distance between the two lines.
Note on the Data
The population data above comes from the U.S. Census conducted every ten years and is therefore generally considered reliable, to the extent that is used as reference for various government programs and voter districting.
The labor force and unemployment data, however, derives from the New England City and Town Areas (NECTAS) segment of the Local Area Unemployment Statistics (LAUS) of the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). A detailed summary of the methodology is not readily available, but in basic terms, it is a model based on and benchmarked to several public surveys. It can be assumed that the sample rate (i.e., the number of people actually surveyed) in each Rhode Island town is very small (averaging roughly 30 people per municipality).
The trends shown, it must be emphasized, are most appropriately seen as trends in the model that generally relate to what’s actually happening among the population but are not an immediate reflection of it. Taking action on the assumption that the exact number of employed or unemployed residents shown corresponds directly to real people in a town would vest much too much confidence in the model’s accuracy.
Be that as it may, the data has been collected and published, and taken a town at a time, it is relatively easy to digest. So, curiosity leads the Current to see it as the best available data to deepen our understanding of trends within Rhode Island. If the findings comport with readers’ sense of how the towns relate to each other, perhaps lessons regarding local and statewide policies may be drawn. If not, then the lesson will be on the limitations of data in our era of information overload.